Introduction
RRC stands for Radio Resource Control. At a broad level, RRC can be defined as a language that should be understood by both Network and UE. As you might be aware that UE and Network communicate via a radio channel. To make the real data exchange possible, every party participating in the communication should exchange a lot of information.
The purpose of communication is to exchange data between the parties and to make this happen, there are a lot of issues that need to be configured.
In the scenario of low - end communication system, the common configuration (about which, we have just discussed) has to be done before the product is released into the market and once it gets released, this configuration will not change.
However, in the scenario of the high-end communication system (for example, cellular communication), this configuration adjusts itself at the time of communication that is, it changes dynamically for optimal result. Now the question that arises is how will both the communicating parties reach a mutual agreement for the common configuration. For this, we require a special control mechanism for the exchange of information between communicating parties on that configuration. This implementation of the control mechanism is called RRC (Radio Resource Control).
There are various other roles that RRC plays for communication within UE and Network. One of them being able to work as a control center for all of the lower layers within each system. The collection of all the lower layers within the UE or the base station is called 'Radio Resource', that is the resources required to make radio communication possible.
Another role is to control and configure all the Radio Resources (PHY, MAC, RLC, PDCP) so that it becomes convenient to communicate between UE and the base station (for example, gNB, eNB, NB, BTS, etc).
Now let us discuss RRC in NR. We will try to cover the structure of RRC and its functions here.
RRC States in NR
The behavior of RRC in NR is shown in the below diagram. Hope you can identify the differences from LTE RRC. You can observe that in NR, a new block (state) has been introduced. It is 'NR RRC INACTIVE'. Complete details of this state are not yet defined in the specifications.
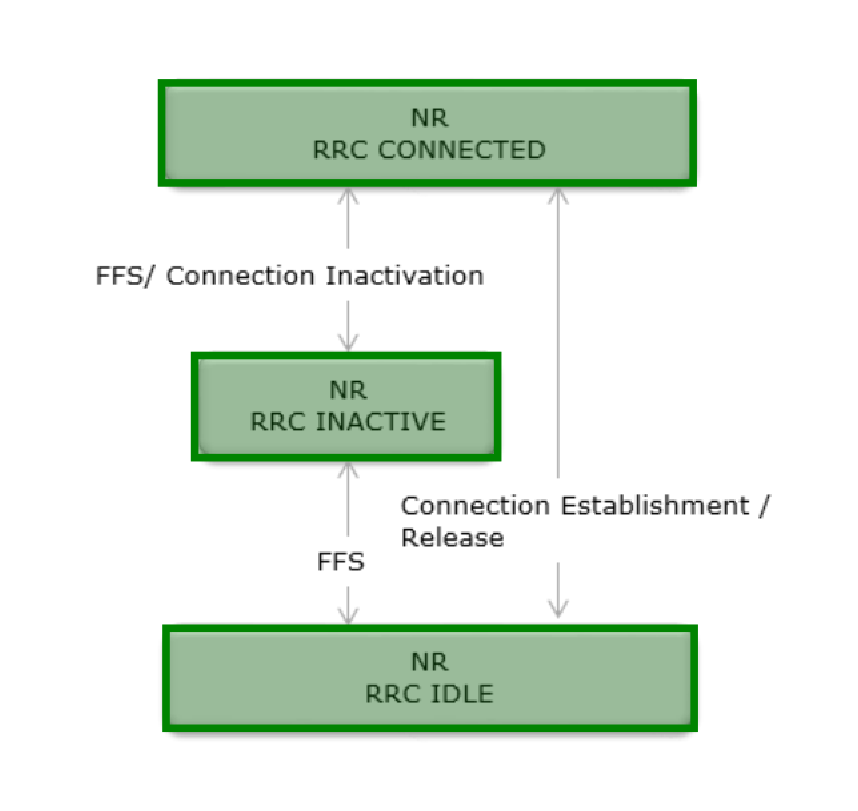
TR 38.804- Figure 5.5.2-1 : UE state machine and state transitions in NR
Let us now discuss NR RRC interaction with its counterpart in other technology.
We start here with the interaction with LTE RRC.
Interaction of NR RRC with LTE RRC
NR RRC is associated with NR as well as with other radio access technology. Below are a few highlights of the interaction between NR RRC and LTE RRC.
- In the IDLE state, selection of NR and LTE can happen that is, LTE can reselect to NR and NR can reselect to LTE (E-UTRA).
- But in the case when NR is in RRC INACTIVE state, NR RRC INACTIVE can reselect to EUTRA, but EUTRA cannot reselect to NR RRC INACTIVE state
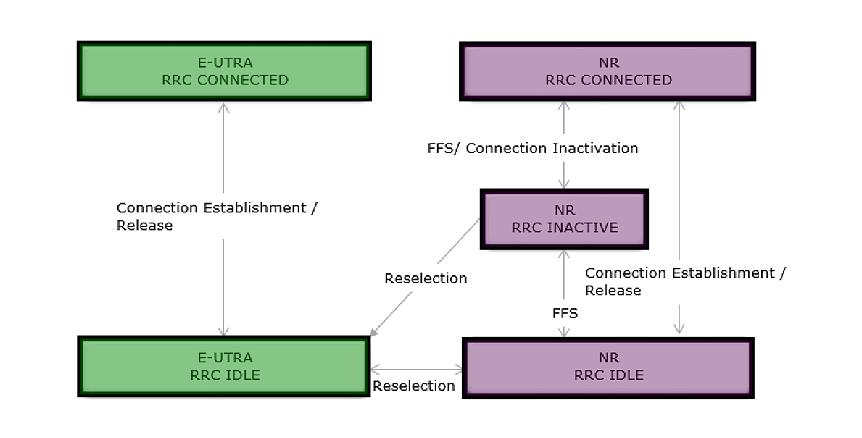
TR 38.804- Figure 10.2-2:UE state machine and state transitions between NR and E-UTRAN
Now we come to the interaction with UTRAN / GERAN RRC.
NR RRC Interaction with UTRAN / GERAN RRC
Below are a few highlights of the interaction between NR RRC and UMTS / GSM RRC.
- In IDLE state, selection of NR and UMTS (UTRA) can happen that is, NR can reselect to UMTS (UTRA) and UMTS can reselect to NR.
- But in the case when NR is in RRC INACTIVE state, NR RRC INACTIVE can reselect to UTRA (UTRA IDLE), but UTRA (UTRA IDLE) cannot reselect to NR RRC INACTIVE state.
- UMTS CELL FACH and CELL/URA PCH can reselect to NR IDLE, but NR IDLE cannot reselect to UMTS CELL FACH or CELL/URA PCH.
- Again when GSM (GERAN) is in IDLE state, NR can reselect to it.
- In IDLE state, GSM can do CCO (Cell Change Order) to NR.
- GPRS can reselect to NR IDLE even while it is in GPRS Packet Transfer Mode.
- GPRS can do CCO to NR IDLE while it is in GPRS Packet Transfer Mode.
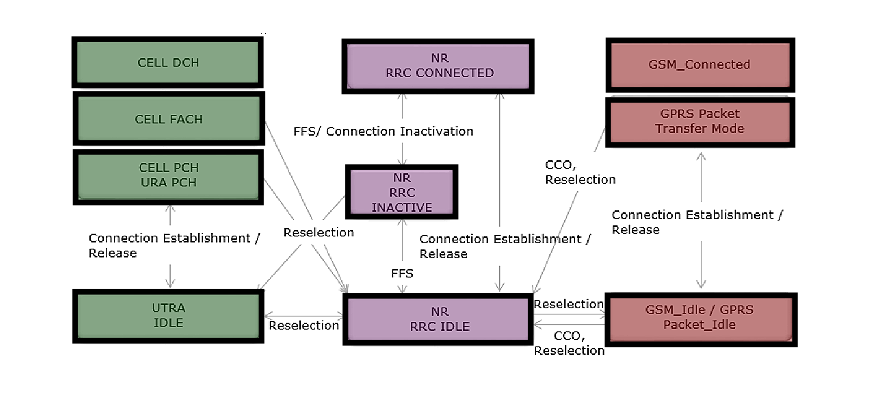
TR 38.804 - Figure 10.2-3:UE state machine and state transitions between NR and UTRAN/GERAN