Introduction
5G, the next generation of cellular networks, currently a very hot topic and an amazing area to learn and research. Be it an end-user, operator, researcher, everyone is interested in knowing about this new technology. There was a time when people communicated using handwritten letters, used to send them manually but now the time has radically changed, we have mobile phones and it is impossible to live without them even for a single day.
For mobile phones to be mobile, the most important and fundamental technology involved is wireless technology. This is what has made our life simple and effortless. The world has completely transformed after the advent of this wonderful technology.
The preceding cellular mobile technologies 4G (4th Generation, known as LTE), 3G (3rd Generation, known as UMTS), 2G (known as GSM) have been deployed successfully in masses all around the world, covering all the geographies. However, with an exponential increase in data demand, the advent of new applications like Augmented Reality (AR), Ultra Fast File Transfer, and Virtual Reality (VR) games which require multi-gigabit data rates, these older technologies are not sufficient.
And this has given birth to the new generation of cellular networks called 5G.
So, let's start with understanding what is 5G.
What is 5G?
5G NR can provide the data rate up to 1 Gbps to the stationary user (in Low mobility) and up to 100 Mbps to the mobile users (in high mobility).
5G enables Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), Ultra-reliable and low latency communications (URLLC), and Massive machine-type communications (mMTC). These use cases are defined by ITU-R (ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R)) and are the three most important use cases for 5G.
Prerequisites for this tutorial
For this 5G tutorial, you will not need any prior experience or knowledge as such. However, some idea about the previous generations of cellular networks (2G (GSM), 3G (UMTS), 4G (LTE)), wireless networks, and computer networks will have some advantage and put the icing on a cake.
Don't worry! We have designed this tutorial keeping you as a beginner in this domain.
Audience
This 5G tutorial is suitable for all the categories of users, irrespective of whether you are a beginner or an expert. We have designed this tutorial series keeping in mind it will give advantage to all the categories of users including and not limited to researchers, professionals, scientists, and students.
At last our aim to share the knowledge of latest technologies and if you are technology enthusiastic, definitely you will enjoy this tutorial.
Now, after understanding what is 5G, few general questions may arise in your mind, which are:
What are the advantages of 5G?
What are the features of 5G?
5G Technology Advantages and Important Features
- Higher system throughput and data rates to end-users.
- Lower the overall power consumption of the network.
- Improve bandwidth.
- Enhance the Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE).
- Provide higher spectral efficiency.
- Increase energy efficiency.
- Improve the coverage for cell-edge users.
- Better security.
- Higher reliability.
- Increase the revenue of network operators and service providers.
- More flexible architecture by making use of SDN (Software Defined Networks) and Network functions virtualization (NFV).
- Provide better interoperability.
- A very good upload and download speed, which will provide an experience like a broadband connection.
- Multiple data transfer paths and sessions
Now, let's discuss 5G important key performance metrics (KPIs) and what are the expected values for these metrics.
5G Key Performance Metrics
| Specification / Feature | 5G Support |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 1 Gbps (Gigabits Per Second) |
| Frequency | 3 GHz to 300 GHz |
| Standard(Access Technologies) | Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) / Beam Division Multiple Access (BDMA) |
| Core Network | 5G network interfacing (5G-NI), Flatter IP network |
| Handoff | Both Horizontal and Vertical |
| Peak Data Rate | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Cell Edge Data Rate | 100 Mbps (Megabits per Second) |
| Latency | Less than 1 millisecond (ms) |
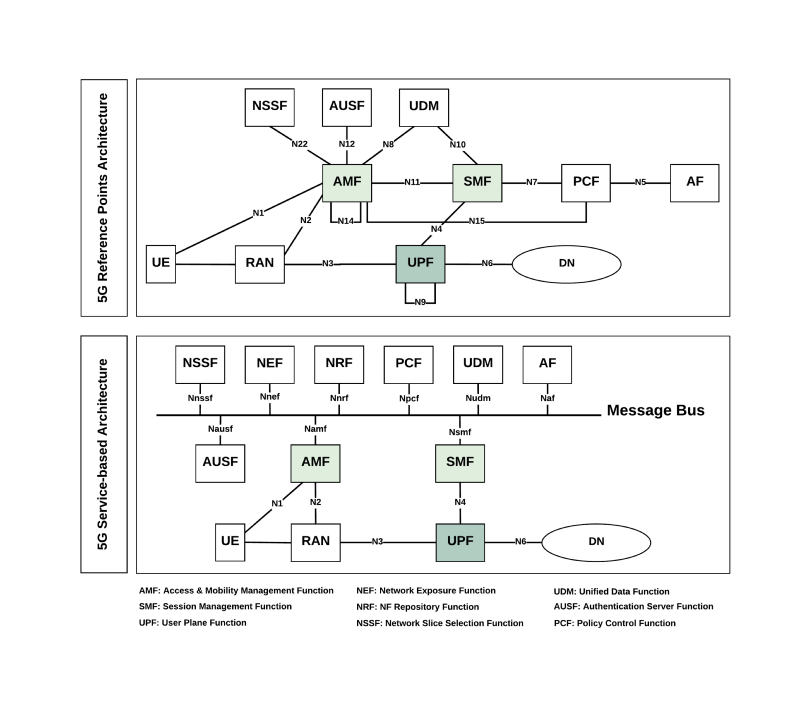
5G NR Architecture
Now, let's discuss the architecture of 5G (NR).
Below is an image of the overall architecture of 5G as per 3GPP specification 3GPP TS 38.300.
5G NR architecture is extremely advanced and very much different from 4G architecture. To tackle several new applications, network elements, interfaces, various other entities are re-designed and fundamentally upgraded. These changes are upgraded in such a way that operators and end-users can get benefitted. On one side, users will get a good quality of service and on the other hand, operators can make more money by incorporating new value-added services.
Below is an image of the overall architecture of 5G as per 3GPP specification 3GPP TS 38.300.
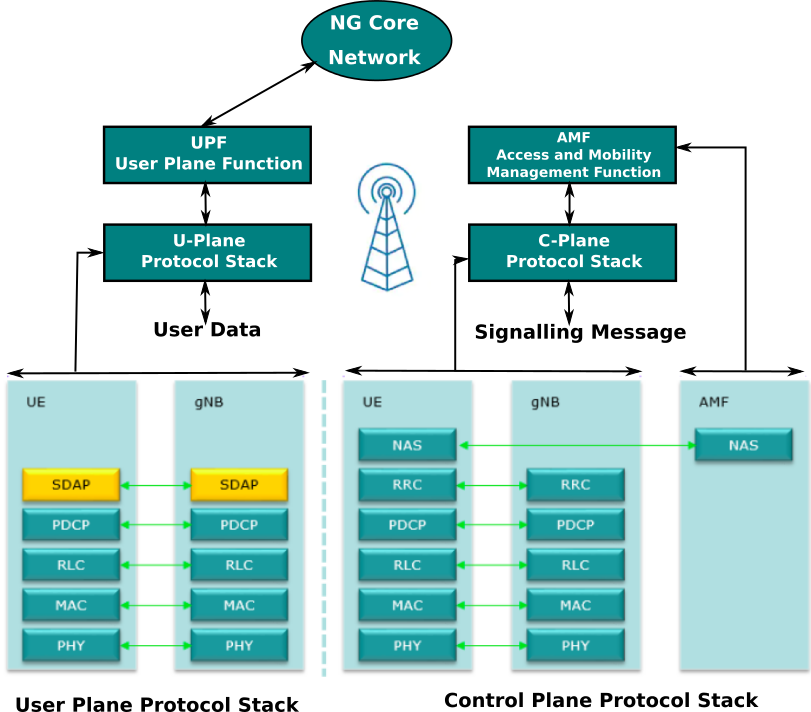
5G NR Protocol Stack
5G protocol or NR protocol stack is very much similar to the LTE (4G) protocol stack. Similar to 4G (LTE), depending upon the direction of data to be processed, 5G radio protocol stack has two categories:
- Control Plane (C-Plane) Stack
- User Plane Stack
Control Plane (C-Plane) Stack
If the type of data is signaling or controlling message, then it is sent/forwarded through the control plane.
User Plane Stack
User data is sent/ forwarded through the user plane.
Stacks of both control and user plane have almost the same structure. They both have the common structure for PHY, MAC, RLC, and PDCP layers as shown in the figure. However, the layers above the PDCP layer are different.
Have a look at the below figures to easily understand and get an overview of it. The main aim is to develop an intuition of how the 5G protocol stack looks like.
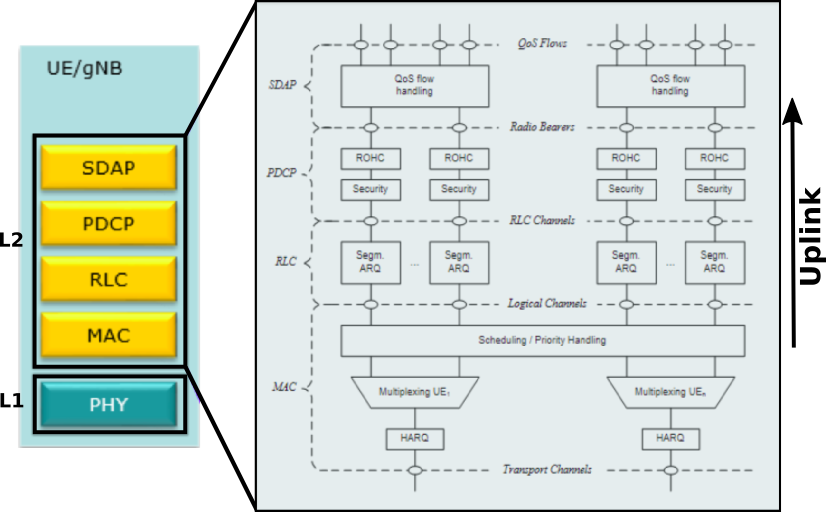
Now, let's go one step deeper and have a look at the internal details of the protocol stack. Below is the figure of downlink L2 (layer 2) stack.
One important thing we can note here that the structure of LTE L2 and NR L2 is very much similar except that one new layer, SDAP, is added in NR. Carrier aggregation is supported in NR from the start. In NR, data for each carrier is processed independently in SDAP layer, PDCP layer, RLC layer and is basically multiplexed in MAC layer.

Now, let's discuss the structure of NR L2 user plane ( U-Plane) uplink protocol. We can observe in the below figure that the basic structure of both uplink and downlink is very much similar. The only major difference is the uplink stack that of downlink stack is it does not have support for carrier aggregation.